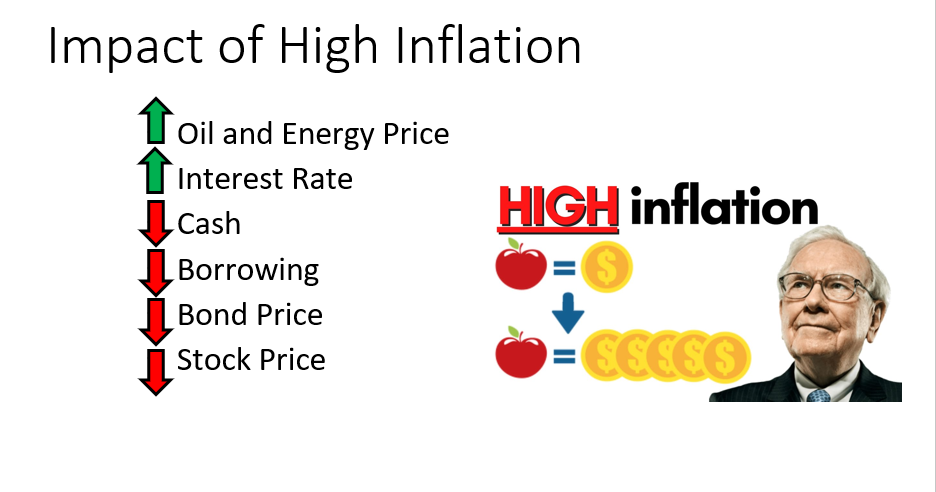
In economics, Inflation means that there is a general increase in prices. It is one of the driving forces in an economy, because inflation means a rise in the price consistently. It’s a good thing for business owners because they make a better profit, but if the consumer doesn’t have inflation in their wages or salary, that’s also not a good thing.
Meaning to say, inflation has a good and bad effect in the economy.
However, if inflation gets out of control, that becomes dangerous. For example, in 1923 in Germany during the First World War, the exchange rate of the mark against the US dollar steadily devalued from 4.2 to 7.9 marks per dollar, a preliminary warning to the extreme postwar inflation. The debt problem was exacerbated by printing money without any economic resources to back it.
Germany began to buy foreign currency with marks at any price, but that only increased the speed of the collapse in value of the mark.

What’s the lesson here
What is the US market at now?
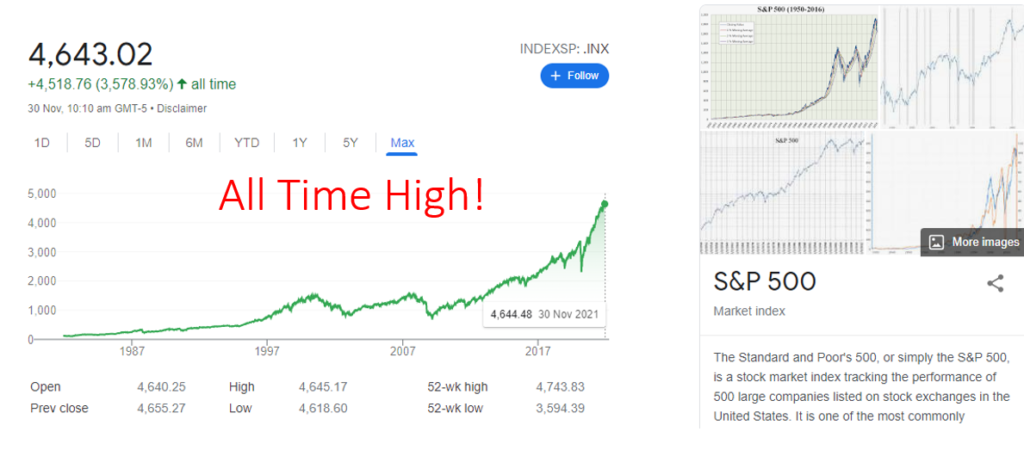
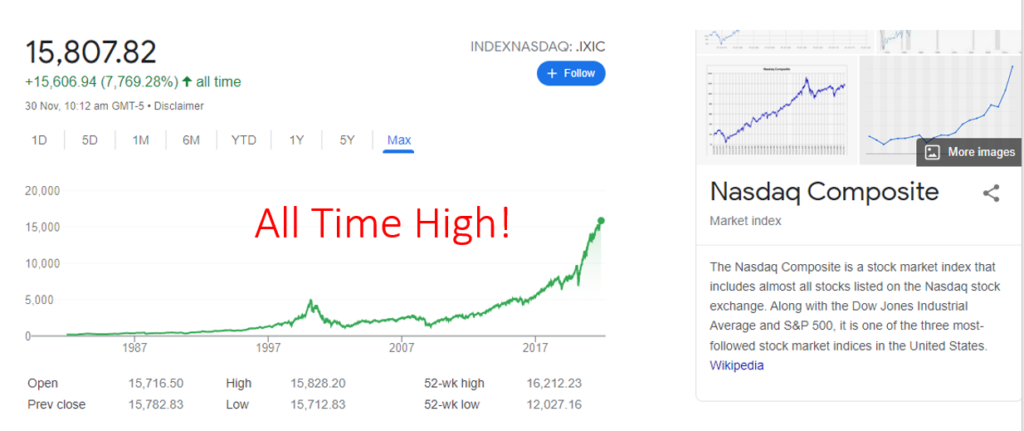
As of 30 Nov 2021, the S& P 500 index tracks the top 500 stocks in the US stock market and the NASDAQ Composite, which tracks the top technology companies in the US. Both are currently at an all time high! When we talk about inflation, capital assets are not included in the “baskets of good” that is calculated. Therefore, how can rely on the current inflation rate reflect the impact on capital assets such as stock prices?

Above diagram shows the global inflation rate displayed in different colors. This is obtained from the quarterly (Q3) JP Morgan Guide to the Markets. The darker the red color the higher inflation rate (above trend) and blue colour shows lower inflation rate (below trend). In 2021, if we compare the inflation rate between the US and China, as highlighted in red box, US inflation since July has been at around 5.4% (above trend) whereas China’s is at around 1.0% (below trend)